Sepsis, a severe condition caused by infections, affects millions of people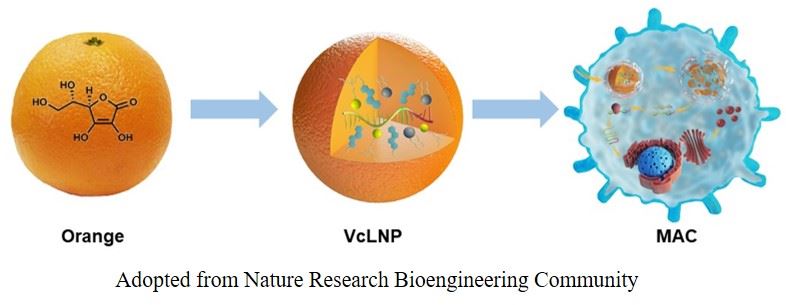 worldwide every year and remains the leading cause of death in hospitals. In addition, multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria have become an additional challenge in the treatment of sepsis and thus, effective therapeutics are urgently needed. A recent paper from Dr. Yizhou Dong and his collaborators at The Ohio State University reported a novel approach for overcoming MDR bacteria-induced sepsis that combines vitamin derived lipid nanoparticles with adoptive macrophage therapy. In this study, the adoptive transfer of macrophages containing antimicrobial peptides in the lysosomes (MACs) reduced bacterial burden and improve survival in the sepsis mouse models. This work was published in Nature Nanotechnology (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0600-1).
worldwide every year and remains the leading cause of death in hospitals. In addition, multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria have become an additional challenge in the treatment of sepsis and thus, effective therapeutics are urgently needed. A recent paper from Dr. Yizhou Dong and his collaborators at The Ohio State University reported a novel approach for overcoming MDR bacteria-induced sepsis that combines vitamin derived lipid nanoparticles with adoptive macrophage therapy. In this study, the adoptive transfer of macrophages containing antimicrobial peptides in the lysosomes (MACs) reduced bacterial burden and improve survival in the sepsis mouse models. This work was published in Nature Nanotechnology (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0600-1).